
Most common allergen sources
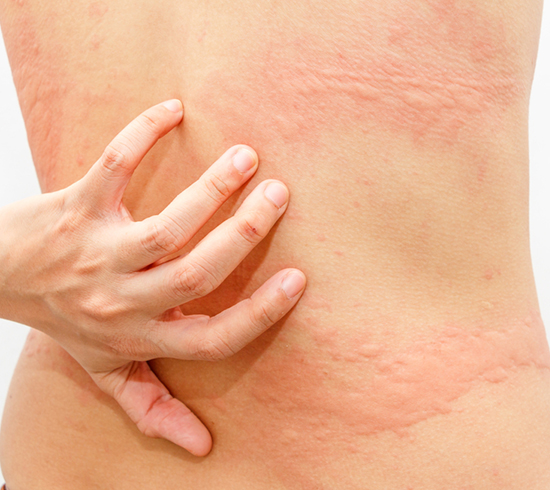

The Symptoms
Onset of the celiac disease may occur during childhood or adulthood with the following symptoms:
- Long lasting or recurring diarrhea/constipation
- Pain in abdomen, abdominal cramps and bloating
- Irritability
- Poor appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Failure to grow normally or delayed growth
- Weight loss or lack of weight gain
- Easy fatigability, exhaustion (lassitude)
- Itchy, blistering skin rash, Urticaria
- Anemia
- Abnormally bulky, pale, frothy stools containing increased levels of fat (steatorrhea)
Treatment of allergies begins with examining the physical symptoms and also takes the following into consideration:
- Life circumstances around the time of onset of the allergy symptoms
- Situations which cause an exacerbation of the allergy symptoms
- Situations which lead to a relief from allergy symptoms
- Feelings aroused by the allergy symptoms, or the person’s unique experience of the condition
- How the allergy symptoms disrupt normal living, or what the person is thereby prevented from doing
- Reaction to changing seasons and which specific is triggered in a weather
The ultimate goal in the healing of allergic symptoms involves eliminating sensitivity while regaining freedom and this is achievable through constitutional treatment primarily through comprehensive systems like homeopathy. With respect to allergies, a healthy person with strong immunity will remain healthy even when exposed to unhealthy influences.
